Selenium Framework Explained: Types and Applications in Automation Testing
Selenium is one of the most popular tools for automating web applications. It provides a suite of tools and libraries that enable testers to automate browser actions, making it easier to perform regression testing, functional testing, and other types of testing. In this blog, we'll explore the different types of Selenium frameworks and their applications in automation testing.
If you want to excel in this career path, then it is recommended that you upgrade your skills and knowledge regularly with the latest Selenium Training in Chennai.
What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source automation tool that allows developers and testers to write scripts in various programming languages, including Java, C#, Python, Ruby, and JavaScript. Selenium supports multiple browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.) and platforms, making it a versatile choice for web application testing.
Types of Selenium Frameworks
1. Selenium WebDriver
Selenium WebDriver is the core component of the Selenium suite. It provides a programming interface to create and execute test cases. WebDriver interacts directly with the browser, mimicking user actions like clicking buttons, entering text, and navigating through pages.
Applications:
- Functional Testing: Validating the functionalities of web applications.
- Cross-Browser Testing: Ensuring compatibility across different browsers.
- Regression Testing: Verifying that new code changes do not adversely affect existing functionalities.
2. Selenium IDE
Selenium IDE (Integrated Development Environment) is a browser extension that allows testers to record and playback tests. It is user-friendly and requires no programming skills, making it ideal for beginners.
Applications:
- Quick Test Creation: Creating simple test cases without writing code.
- Prototyping: Rapidly developing test scripts for demonstration purposes.
- Learning Tool: Helping new testers understand Selenium's capabilities.
With the aid of Selenium Course in Online programs, which offer comprehensive training and job placement support to anyone looking to develop their talents, it’s easier to learn this tool and advance your career.
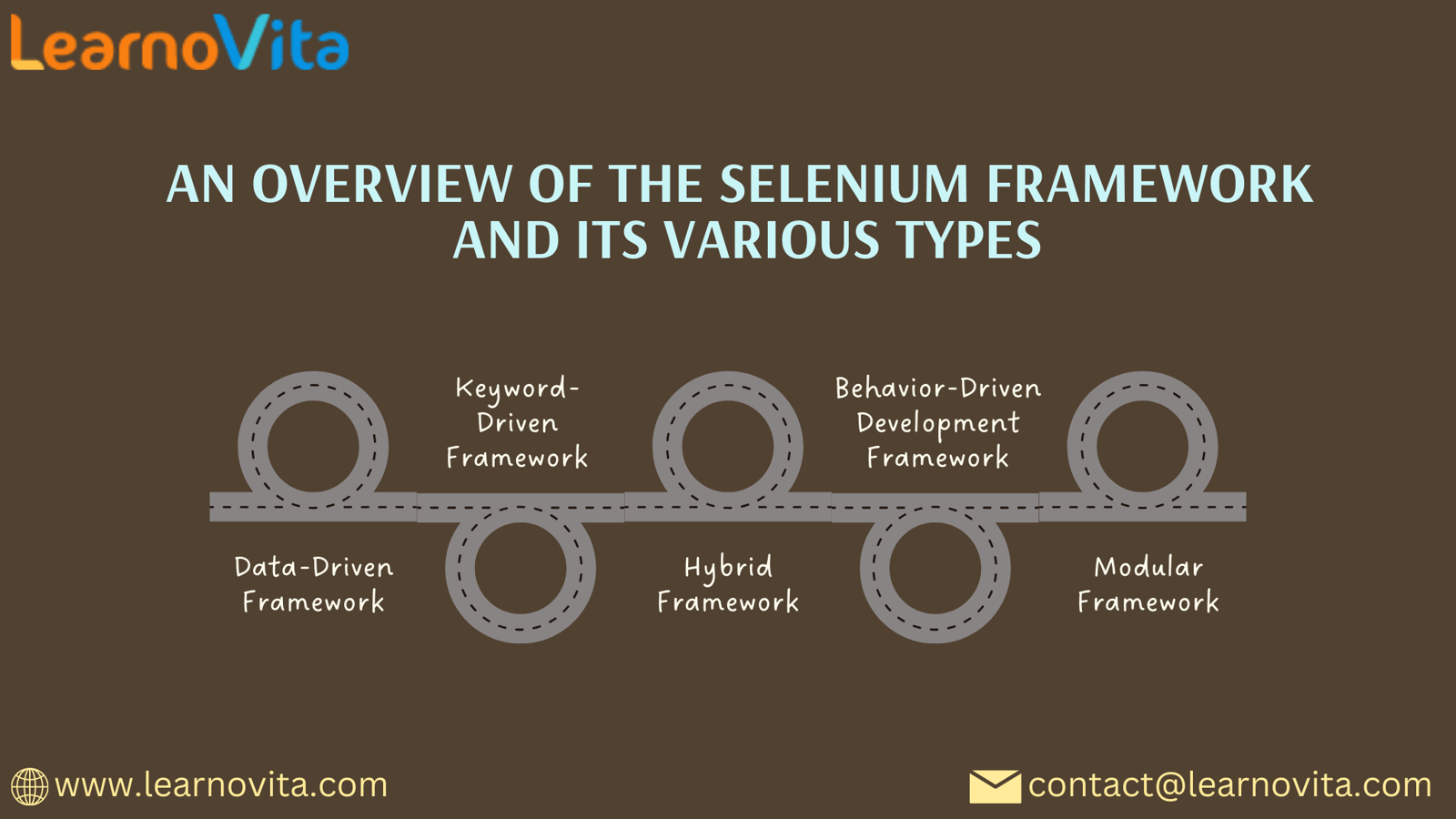
3. Selenium Grid
Selenium Grid is used for parallel testing across multiple machines and browsers. It allows testers to run tests concurrently, significantly reducing the time needed for test execution.
Applications:
- Cross-Platform Testing: Running tests on different operating systems and environments simultaneously.
- Load Testing: Simulating multiple users to check application performance under load.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Maximizing the use of available machines and browsers.
4. Selenium Frameworks (TestNG, JUnit, NUnit)
These frameworks provide a structure for organizing and executing test cases. TestNG (Java), JUnit (Java), and NUnit (.NET) enhance Selenium's capabilities by adding features like parallel test execution, test case management, and reporting.
Applications:
- Test Case Management: Organizing tests into suites and categories.
- Reporting: Generating detailed reports of test results.
- Dependency Management: Handling test dependencies easily.
Benefits of Using Selenium Frameworks
- Open Source: Selenium is free to use, making it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Flexibility: Supports multiple programming languages and frameworks.
- Community Support: A large community of users provides extensive resources and support.
- Integration: Easily integrates with various tools for CI/CD, test management, and reporting.
Conclusion
Selenium remains a powerful tool for automation testing due to its flexibility, ease of use, and robust community support. Understanding the different types of Selenium frameworks and their applications is crucial for leveraging the full potential of this tool in your testing efforts. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced tester, Selenium offers a variety of options to help you automate your web application testing efficiently.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Παιχνίδια
- Gardening
- Health
- Κεντρική Σελίδα
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- άλλο
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



