Coding with Python: From First Steps to Mastery

Python has become one of the most in-demand programming languages today. Its simple syntax, flexibility, and huge library support make it perfect for both beginners and experienced programmers. Whether you want to start coding for the first time or expand your technical skills, Python Course in Bangalore is a powerful choice.
Here’s a step-by-step roadmap to guide you from beginner to confident Python developer.
Step 1: Start With the Basics
Begin by learning Python’s core concepts:
- Syntax and variables
- Data types like strings, numbers, and lists
- Loops and conditionals
- Input/output and error handling
Reinforce these topics with online tutorials and hands-on exercises. Building a strong foundation now will make advanced topics much easier later.
Step 2: Set Up Your Environment
Download Python from the official site and choose an editor or IDE that suits you VS Code, PyCharm, or the built-in IDLE. For interactive coding, try Jupyter Notebook.
- Use pip or conda to install packages.
- Create virtual environments to keep projects organized.
- Experiment with online tools like Google Colab or Replit if you prefer coding in the browser.
- A good setup will make coding smoother and more efficient.
Step 3: Learn Data Structures and Algorithms
Get familiar with Python Course Online Training built-in data structures: lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets. Learn how to manipulate them effectively, then practice common algorithms like sorting and searching. This step builds the problem-solving skills you’ll need as a developer.
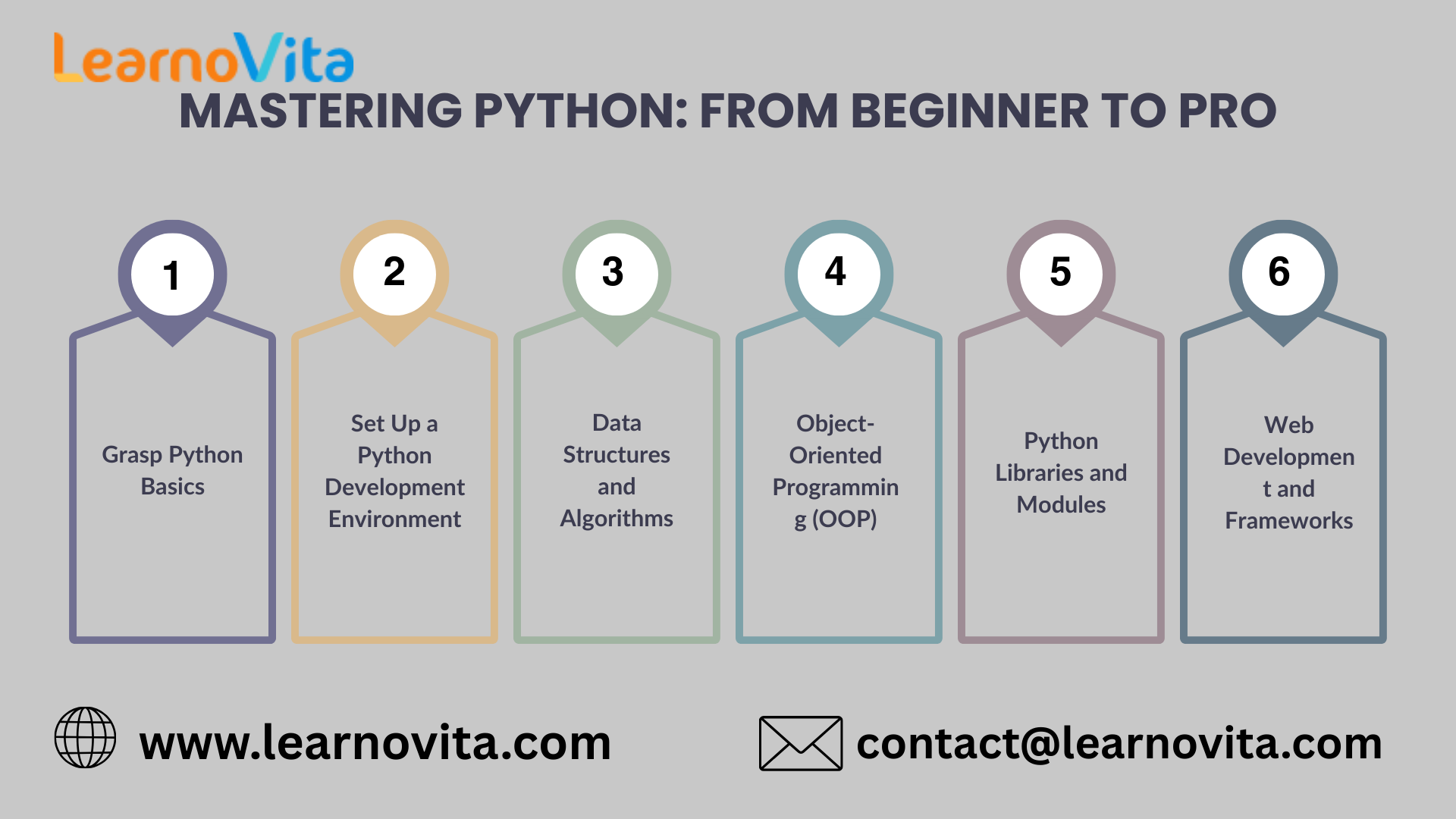
Step 4: Understand Object-Oriented Programming
OOP is essential for writing scalable and reusable code. Learn how to:
- Create classes and objects
- Use encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism
- Apply best practices to keep your code organized and maintainable
- Practice these concepts by building small, practical projects.
Step 5: Explore Popular Libraries
Python’s ecosystem of libraries is what makes it so powerful. Start with:
- NumPy: numerical computing
- Pandas: data analysis
- Matplotlib / Seaborn / Plotly: data visualization
- SciPy: scientific computing
As you grow, branch into libraries based on your goals—machine learning, automation, web scraping, or beyond.
Step 6: Build Web Applications
- Python is widely used in web development.
- Try Flask for small projects and APIs.
- Learn Django if you want to create full-scale applications.
Along the way, explore databases, REST APIs, and deployment methods to bring your applications to life.
Final Thoughts
Becoming proficient in Python takes consistent practice, not speed. By following these steps mastering the basics, practicing data structures and OOP, exploring libraries, and building projects you’ll be well on your way to using Python confidently in real-world applications.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



