A Developer’s Handbook to AWS Lambda and Modern Serverless Architecture
The emergence of serverless computing has transformed the way applications are built, deployed, and maintained. Unlike traditional infrastructure models that require constant server management, serverless technology allows developers to focus solely on writing and deploying code. Among the leading innovations driving this shift, AWS Lambda stands out as a key enabler of scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions. It allows applications to run in response to events without the need to manage servers, offering automatic scaling, flexibility, and efficiency. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamentals of AWS Lambda, its relationship with serverless architecture, its benefits, and best practices that empower developers to maximize its potential. Enhance your cloud computing skills and boost your career with AWS Training in Chennai, designed to help you master core AWS services, cloud architecture, and real-world deployment strategies.

Understanding Serverless Architecture
Serverless architecture is a cloud-based approach where infrastructure management is completely handled by the cloud provider. Developers no longer need to provision or maintain servers manually. Instead, their applications are divided into independent functions that execute automatically when specific events occur, such as database updates, file uploads, or API calls. This model provides several advantages: it scales automatically with demand, charges only for the time the code runs, and eliminates idle resource costs. Beyond cost savings, serverless computing enhances agility, allowing teams to build modular, maintainable systems where each component can evolve or scale independently without disrupting the rest of the application.
An Overview of AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda, Amazon’s premier serverless compute service, enables developers to run their code in response to predefined triggers without managing any infrastructure. After uploading code and defining event sources, AWS Lambda automatically handles provisioning, scaling, and monitoring. The service supports multiple programming languages, such as Python, Java, Node.js, and C#, making it widely accessible. When a triggering event occurs (like a file upload or an HTTP request), Lambda executes the corresponding function instantly, scales based on demand, and stops running once the process completes. Its pay-per-execution model ensures that users are billed only for the actual compute time consumed, making it both efficient and cost-effective.
How AWS Lambda Operates
AWS Lambda functions are designed to be event-driven and stateless, meaning they run independently without retaining data between executions. When a trigger event, such as a database change or an API call, occurs, AWS automatically sets up a secure runtime environment for the Lambda function. The system seamlessly scales to accommodate multiple requests simultaneously and then terminates resources after execution, ensuring there are no unnecessary costs for idle time. Lambda’s integration with AWS services such as Amazon S3, DynamoDB, CloudWatch, and API Gateway allows developers to create automated workflows that support web applications, analytics, IoT solutions, and more, all without managing underlying servers.
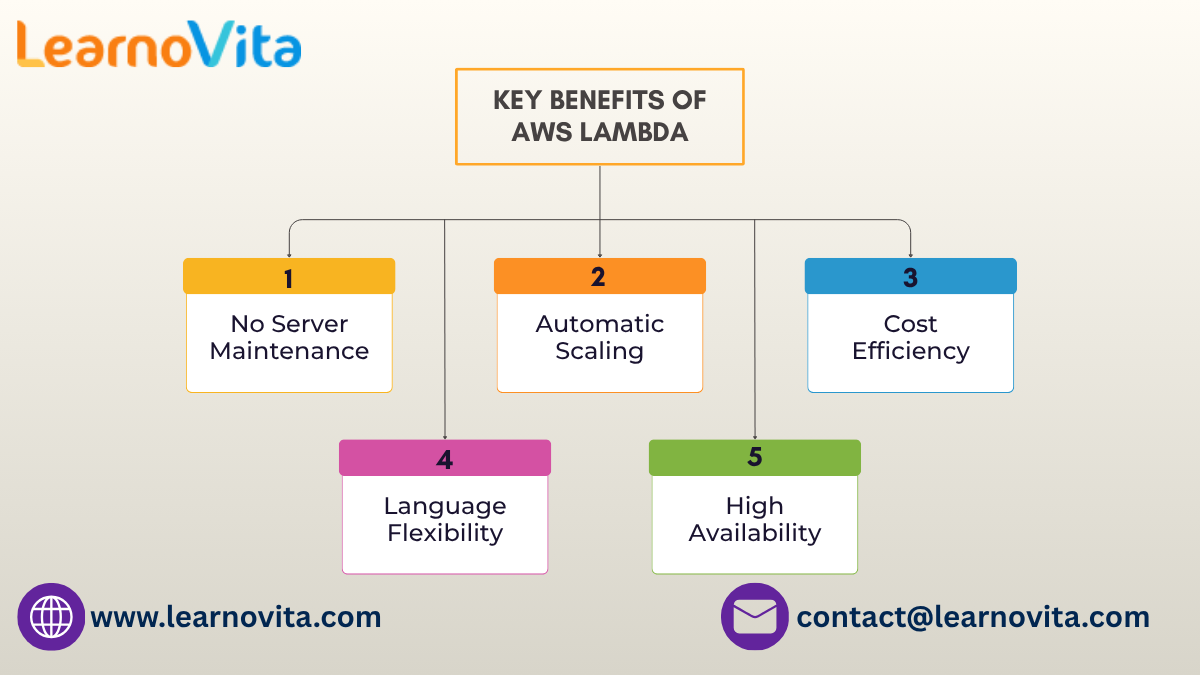
Key Advantages of AWS Lambda
-
No Server Management: AWS handles provisioning, scaling, and infrastructure updates automatically.
-
Auto Scaling: Functions scale instantly to meet fluctuating demand.
-
Cost Efficiency: Billing is based solely on execution time and resources used.
-
Flexible Language Support: Works seamlessly with multiple programming environments.
-
High Reliability: Built on AWS’s fault-tolerant and globally distributed infrastructure.
The AWS Certification Course is designed to equip learners with in-demand cloud skills and prepare them for globally recognized AWS certification exams.
Practical Applications of AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda has become an integral tool across various domains and industries. It powers backend logic for web and mobile applications through API Gateway integration, offering scalable and fast responses without traditional servers. It’s widely used in data processing workflows, where Lambda can automatically resize images, process logs, or transform data when new files are added to Amazon S3. In IoT environments, Lambda handles real-time device data, enabling intelligent and responsive systems. Additionally, DevOps teams utilize Lambda for automation, executing scheduled tasks, cleaning up unused resources, or managing deployment pipelines. These use cases demonstrate how Lambda simplifies cloud operations while enabling innovation.
Best Practices for AWS Lambda Implementation
-
Keep Functions Modular: Each function should perform one focused, specific task for clarity and reusability.
-
Use Environment Variables: Store credentials and configuration settings securely instead of embedding them in the code.
-
Monitor Performance: Leverage Amazon CloudWatch to track metrics, execution time, and potential errors.
-
Organize Dependencies: Utilize AWS Lambda Layers to manage shared libraries efficiently across multiple functions.
-
Strengthen Error Handling: Implement retry mechanisms and fallback workflows to ensure reliability.
-
Optimize Cold Starts: Minimize function size and dependencies to improve startup speed.
Conclusion
AWS Lambda has redefined how cloud applications are created, scaled, and maintained. By removing the burden of infrastructure management, it allows developers to focus on functionality, performance, and innovation. When combined with a serverless architecture, Lambda provides unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. From powering real-time analytics and data automation to enabling backend services for web applications, its versatility makes it a foundational element in today’s cloud ecosystem. As organizations continue to move toward cloud-native solutions, mastering AWS Lambda will be crucial for developers aiming to build fast, efficient, and future-ready applications. In essence, AWS Lambda is not just a service, it’s the cornerstone of the next generation of cloud computing.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- الألعاب
- Gardening
- Health
- الرئيسية
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- أخرى
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



