Introduction to Blockchain A Beginners Overview of Decentralized Technology
Blockchain is an emerging digital framework that's redefining how information is shared and stored. Originally introduced through Bitcoin, its purpose now stretches far beyond cryptocurrencies. Simply put, blockchain is a series of connected digital records blocks arranged in chronological order and maintained by a network of users rather than a single authority. This decentralized model ensures transparency, security, and trust in digital interactions.
Importance of Decentralized Systems
Decentralization is what separates blockchain from traditional systems. Instead of relying on one organization to oversee and validate data, blockchain spreads that responsibility across a wide network of users, or nodes. Each node has equal access to the full database and plays a role in validating new entries. This distributed nature makes it difficult to tamper with, increases system resilience, and eliminates reliance on a central gatekeeper. Master the fundamentals of blockchain technology with our Blockchain Online Course designed for beginners and professionals alike.

Key Characteristics of Blockchain
The unique qualities of blockchain that make it so powerful include:
-
Immutability: Once added, data cannot be changed or erased.
-
Transparency: Every transaction can be traced and verified by participants.
-
Decentralized Security: Data is encrypted and validated across the network.
-
Shared Responsibility: No single point of failure or control.
-
Elimination of Intermediaries: Direct transactions reduce delays and extra costs.
How Blockchain Actually Works
Blockchain operates by recording data into blocks, each one linked to the previous in a secure chain. When a transaction occurs, it's verified by network participants through a consensus mechanism. Once validated, the transaction is added to a block and that block joins the chain permanently. This process creates a trusted environment where records are secure, consistent, and visible to all authorized users, without needing a central administrator.
Different Types of Blockchain Networks
Blockchain systems come in various forms based on how they’re controlled and accessed:
-
Public Blockchains: Open for anyone to use and fully transparent.
-
Private Blockchains: Restricted to specific participants, often used within organizations.
-
Consortium Blockchains: Controlled by a group of entities with shared interests.
Applications of Blockchain in the Real World
Blockchain is no longer limited to finance, it’s finding practical uses across industries. In logistics, it provides transparent tracking of shipments, reducing fraud and inefficiency. Financial institutions are using it for quicker cross-border transactions. In the healthcare sector, blockchain enables secure patient record sharing. Government bodies are also testing blockchain to digitize land records, enhance voting systems, and increase public transparency. Our Best Training & Placement Program ensures hands-on learning and career support, guiding you from skill-building to securing your dream job.
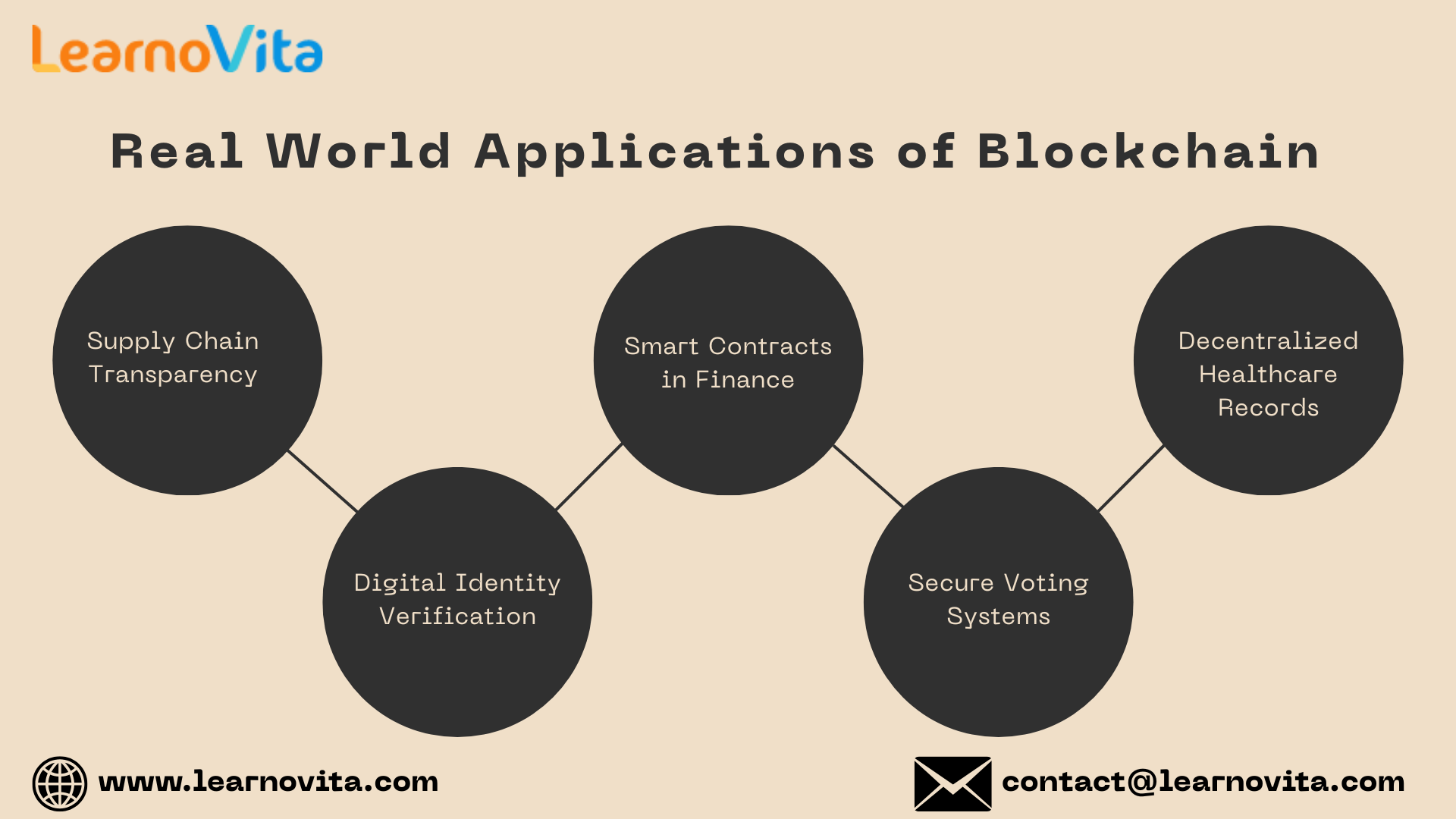
Smart Contracts and Automation on Blockchain
Smart contracts are self-executing digital agreements stored on a blockchain. These contracts automatically fulfill terms once conditions are met no human involvement required. For instance, in real estate, a smart contract can release funds when a title transfer is confirmed. They're widely used today to simplify processes in sectors like insurance, logistics, and digital identity verification, bringing speed, trust, and efficiency.
Current Challenges with Blockchain Adoption
Despite its growing adoption, blockchain faces a few limitations. Public blockchains often struggle with performance issues as they grow in size and usage. High energy consumption is another challenge, especially with older consensus models like proof-of-work. In addition, many countries are still drafting blockchain regulations, which creates uncertainty. Integrating blockchain with traditional systems also requires specialized skills and significant investment.
Future of Blockchain and Emerging Trends
Blockchain is steadily evolving. New protocols are being designed to improve scalability and reduce environmental impact such as proof-of-stake and zero-knowledge proofs. Integration with AI and IoT is also expanding blockchain’s capabilities into predictive analytics and real-time automation. Looking ahead, blockchain is expected to be a foundational layer for decentralized apps, digital ID systems, and next-generation internet infrastructure.
Closing Thoughts
Blockchain represents a major shift in how we manage digital information. It brings transparency, trust, and efficiency to systems that traditionally rely on central authorities. For those just starting out, understanding blockchain’s core ideas opens the door to future-ready careers and innovations. As more industries turn to decentralized technologies, now is the right time to explore and build your knowledge around blockchain.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



