PARSABIV (Etelcalcetide Hydrochloride Injection) – Mechanism of Action and Dosage
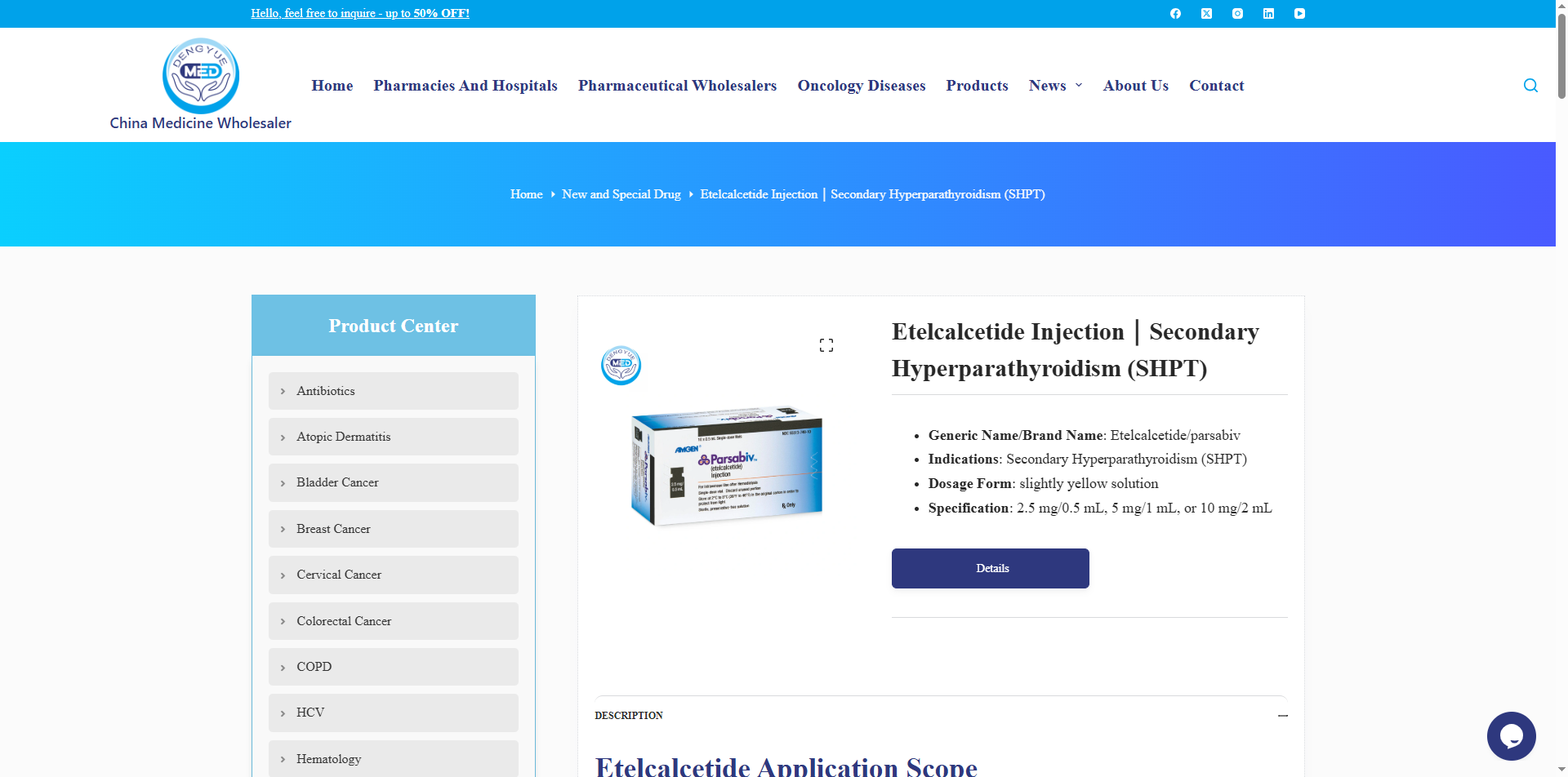
Below is a detailed description of the mechanism of action and dosage of PARSABIV (Etelcalcetide Hydrochloride Injection):
Mechanism of Action
PARSABIV is a synthetic calcimimetic peptide drug. Its active ingredient, etelcalcetide, specifically binds to and activates the calcium-sensing receptors (CaSR) on the surface of parathyroid cells. By mimicking the physiological effects of increased serum calcium, it suppresses parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion. This mechanism simultaneously reduces serum calcium and phosphate levels, improving mineral metabolism disorders in patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT).
Dosage and Administration
1. Formulation and Strength
Injection formulations:
-
0.5 ml: 2.5 mg (single-dose vial)
-
1 ml: 5 mg (pre-filled syringe)
-
2 ml: 10 mg (amber glass light-protected vial)
Characteristics: Clear, colorless solution, pH 7.4, citrate buffer; store at 2–8 °C protected from light.
2. Dosing Regimen
-
Initial dose: 5 mg intravenous bolus, three times weekly (administered at the end of dialysis), injection duration ≥1 minute.
-
Dose adjustment: Adjust in 2.5 mg or 5 mg increments based on PTH and corrected serum calcium, up to a maximum dose of 15 mg/week.
-
Adjustment interval: ≥4 weeks
-
Target PTH range: 150–300 pg/mL (as recommended by KDIGO guidelines).
-
-
Special populations: For patients weighing <50 kg, a starting dose of 2.5 mg is recommended.
3. Administration Considerations
-
Monitoring requirements:
-
Corrected serum calcium (weekly), PTH (monthly), phosphate (every 2 weeks).
-
Closely monitor ECG changes after first administration or dose adjustment.
-
-
Administration method:
-
Must be injected into the arterial line of the dialysis circuit; do not mix with calcium-containing solutions.
-
-
Missed dose: If a dialysis session is missed, no supplementation is required; continue with the usual dose at the next dialysis session.
Adverse Reactions
Common adverse reactions include hypocalcemia (requiring immediate calcium supplementation), muscle cramps, diarrhea, and nausea. In terms of cardiovascular benefits, a ≥30% reduction in FGF23 has been associated with an 18% lower risk of major cardiovascular events.
Note: This information was compiled and edited by Hong Kong DengYue Medicine. It provides updates on the latest globally marketed drugs. For specific prescribing guidance, please consult your physician.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Autre
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



