Harnessing the Power of Data Through Advanced SQL Functions
In today’s digital-first world, organizations collect vast amounts of information every second. But raw data by itself doesn’t create value it’s the ability to analyze, interpret, and act on that data that drives results. SQL (Structured Query Language) remains one of the most reliable tools for this purpose. Most professionals are familiar with basic SQL commands such as SELECT, INSERT, and UPDATE. These are great for everyday data handling, but when businesses need deeper insights, advanced SQL Course in Bangalore functions come into play. They help transform complex datasets into clear, actionable information and unlock opportunities hidden within the numbers.
Why Advanced SQL Functions Are Essential
Advanced functions make it possible to perform detailed analysis directly within a database. Instead of moving data to external tools or relying on lengthy processes, SQL lets you process and analyze information where it already resides. This approach saves time, improves efficiency, and ensures accuracy, especially with large datasets.
Key Types of Advanced SQL Functions
1. Aggregate Functions
Aggregate functions provide summaries that reveal the bigger picture. With commands like SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MIN(), and MAX(), you can quickly calculate totals, find averages, or spot extremes. For example, finance teams can track total expenses while retailers measure average purchase values.
2. Window Functions
Window functions are powerful because they let you compare rows while keeping detailed data intact. Functions such as ROW_NUMBER(), RANK(), LEAD(), and LAG() are useful for identifying top performers, ranking results, and spotting changes over time. Businesses often use them to measure customer loyalty or monitor month-over-month growth.
3. String Functions
Data often comes in unstructured or messy formats. String functions like CONCAT(), SUBSTRING(), REPLACE(), and TRIM() make it easier to clean and format text. For instance, SQL Online Course marketers can extract domains from email addresses or standardize customer names for reporting.
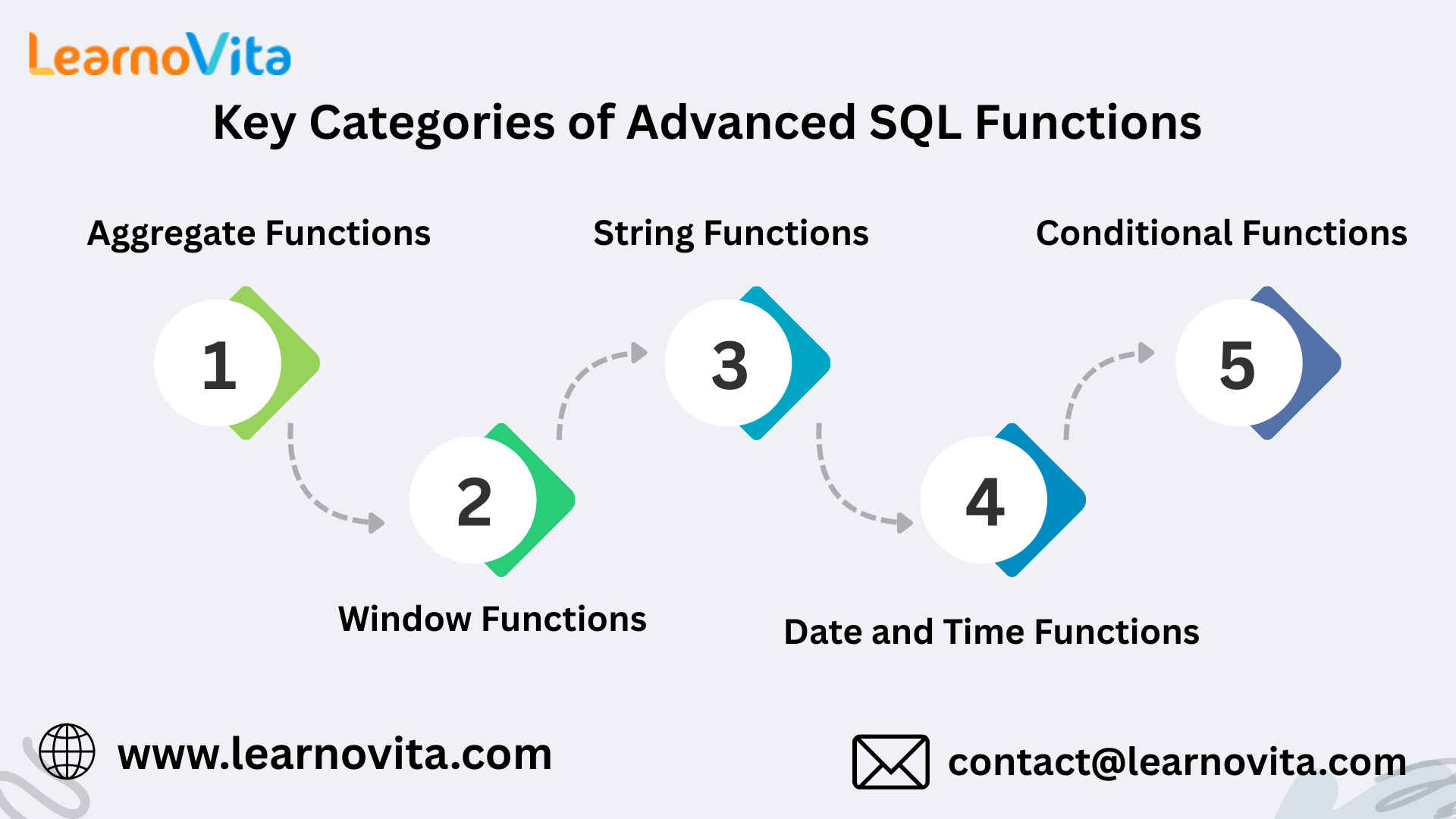
4. Date and Time Functions
Timing matters in every industry. SQL’s DATEDIFF(), DATEADD(), and NOW() functions help track intervals, project future timelines, and reveal seasonal patterns. A healthcare provider could use these to monitor patient follow-up intervals, while e-commerce platforms might study sales during holidays.
5. Conditional Functions
Conditional logic gives SQL more flexibility. The CASE statement allows users to build rules into queries and categorize data on the fly. For example, businesses can group customers into categories like “Premium,” “Regular,” or “Occasional” based on spending behavior.
Real-World Impact
The benefits of advanced SQL functions cut across industries:
-
Banking: Detecting fraudulent transactions and ranking portfolios.
-
Retail: Forecasting demand and understanding purchase cycles.
-
Healthcare: Tracking patient records and resource usage.
-
Marketing: Personalizing campaigns with customer segmentation.
Conclusion
Basic SQL queries help retrieve data. Advanced SQL functions help you understand and act on it. By learning how to use aggregates, windows, strings, dates, and conditional logic, professionals can uncover insights that fuel smarter strategies and better business outcomes. Simply put, mastering advanced SQL functions is the key to unlocking the full potential of your data.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Игры
- Gardening
- Health
- Главная
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Другое
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



