SQL as the Backbone of Business Intelligence Systems
Data has become one of the most valuable assets for modern organizations. From customer transactions to supply chain records, businesses generate information every second. Yet raw data doesn’t automatically create value. It needs to be processed, structured, and interpreted before it can guide decisions. That is the role of Business Intelligence (BI) and at the heart of BI lies SQL Course in Chennai, or Structured Query Language.
Why SQL Is Critical for BI
Most enterprise data is stored in relational databases, and SQL is the universal language for retrieving and managing it. While BI tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Looker provide polished dashboards and visualizations, SQL ensures that the underlying data is accurate, consistent, and ready for analysis. It acts as the essential bridge between complex databases and the insights decision-makers need.
How SQL Powers BI and Reporting
1. Extracting and Preparing Data
Data is often scattered across different systems sales platforms, finance applications, and HR databases. SQL makes it possible to pull these pieces together, merge them with JOIN operations, or reorganize them with commands like GROUP BY. This step ensures analysts work with a complete and clean dataset.
2. Creating Reliable Reports
Reports form the backbone of business decision-making. Whether it’s tracking monthly sales, monitoring cash flow, or measuring employee productivity, SQL queries power the numbers behind the charts. These queries guarantee accuracy and help organizations maintain confidence in their reporting.
3. Fueling Dashboards and Visuals
Interactive dashboards depend on SQL to fetch live data from databases. Every graph or KPI refreshes because of a query running in the background. Well-designed SQL not only speeds up these dashboards but also ensures that leaders see the most up-to-date information.
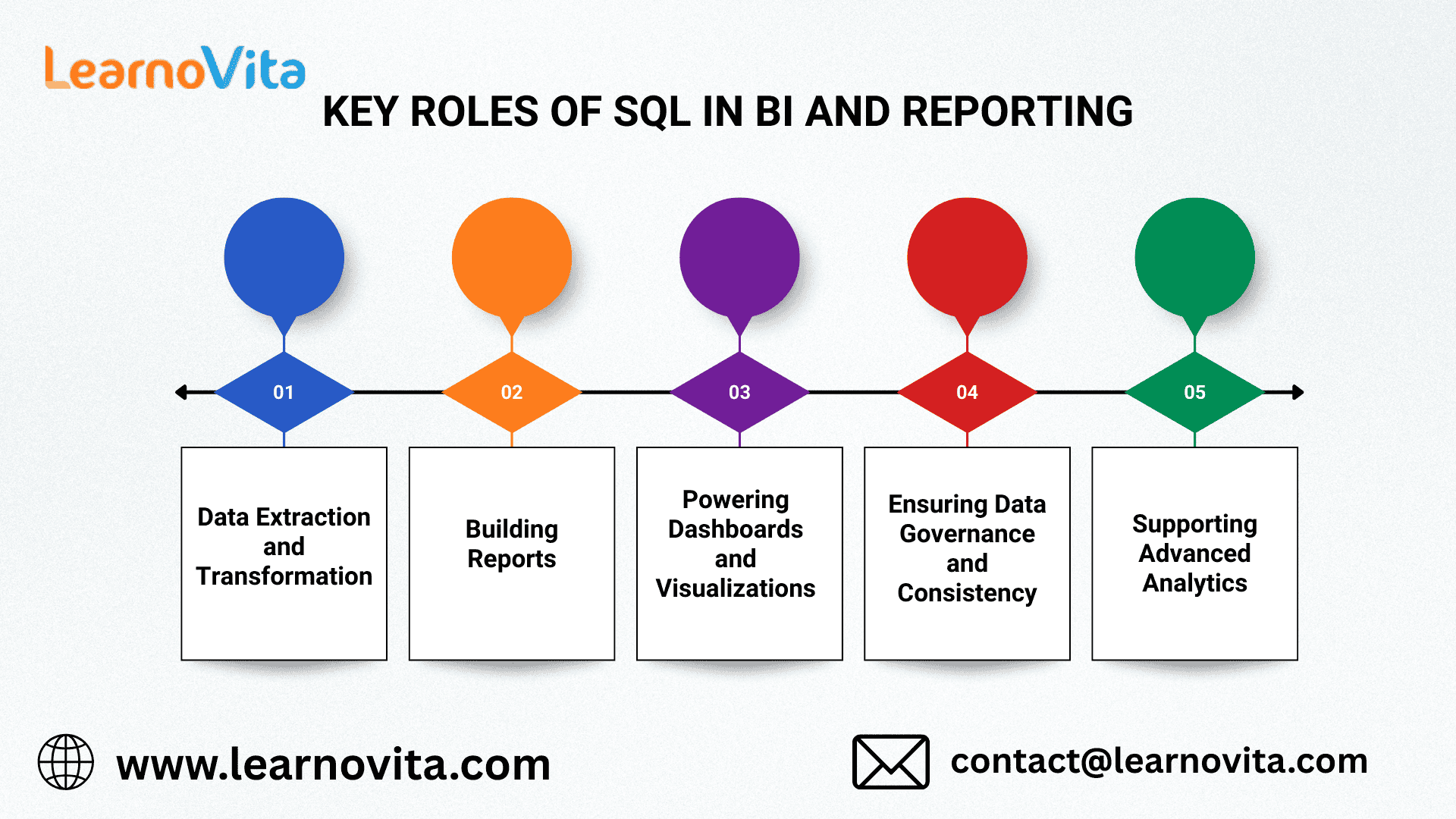
4. Maintaining Data Consistency
In large organizations, different departments often build reports independently, which can lead to conflicting results. SQL Online Course allows BI teams to define standard views and queries that everyone can use, ensuring consistency and alignment across the company.
5. Enabling Advanced Analysis
SQL is more powerful than basic queries. With advanced features such as window functions, Common Table Expressions (CTEs), and subqueries, analysts can run complex calculations within the database itself. This capability accelerates analytics and reduces the need for additional tools.
SQL as the Foundation of BI
While cloud platforms, NoSQL databases, and AI-driven tools are expanding the data landscape, SQL continues to be the backbone of BI and reporting. Its simplicity, universality, and efficiency make it a skill every BI professional must master.
Conclusion
SQL plays a central role in Business Intelligence by enabling accurate reporting, interactive dashboards, and advanced analytics. It ensures that organizations move beyond raw data and unlock insights that drive performance and growth. For any business investing in BI, SQL remains not just a technical requirement but a strategic advantage.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spellen
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



