How Does Maven Handle Selenium Dependencies?
Introduction
Modern software teams test web applications in fast development cycles. Testers need tools that support quick setup, easy scaling, and smooth integration. Selenium solves browser automation needs, and Maven solves dependency management needs. Many beginners join an Online Selenium training program or a Selenium certification course and quickly discover that Maven plays a major role in professional test automation. Maven helps teams manage Selenium libraries, plug-ins, project structure, and build life cycles. Testers use Maven because it gives simple control over Selenium versions. Maven also helps testers avoid long manual setup steps.
This blog explains how Maven handles Selenium dependencies in a clear and practical way. You will see real examples, simple explanations, and steps that help you apply these ideas in your test projects. You will find this guide useful if you are learning through a Selenium course online, Selenium online training, or any Selenium automation testing course. It provides strong fundamentals for anyone entering Selenium automation testing or preparing for automation software training.
Why Testers Use Maven With Selenium
Testers need a stable toolchain for continuous delivery. Maven supports that need. Maven gives dependency management, project build automation, and standardized structure. These features help testers write clean, repeatable, and maintainable tests. Maven reduces manual downloads and version mismatches. It also ensures that all members of a team use the same Selenium libraries.
Industry research shows that more than 78% of automation teams use build tools like Maven or Gradle in enterprise automation pipelines because dependency management saves development time and reduces setup issues. Teams that use Maven report smoother onboarding for new automation testers because a single pom.xml controls everything from Selenium WebDriver downloads to test execution plug-ins.
Students in a Selenium testing course or selenium test automation course see Maven early because it helps them start projects without confusion. Many training instructors highlight Maven because companies prefer testers who can manage test frameworks with professional build tools.
Understanding Maven in Simple Words
Maven is a build automation and dependency management tool for Java projects. It uses a pom.xml file to manage libraries. It uses a repository system to download them. It also uses a structured project layout. Maven controls the build life cycle through simple commands.
To use Selenium in a Maven project, you add Selenium’s dependency code into the pom.xml file. Maven downloads the correct version from its repository and sets it up automatically.
Here is a simple breakdown:
-
Maven stores project structure.
-
Maven reads dependencies.
-
Maven pulls required libraries.
-
Maven resolves version conflicts.
-
Maven supports plug-ins for test execution.
-
Maven integrates easily with CI/CD tools.
This system removes manual setup steps and supports scalable test automation.
How Maven Handles Selenium Dependencies
1. Maven Downloads Selenium Libraries Automatically
You place the Selenium dependency inside the dependencies section of pom.xml. Maven checks local repository storage. If Selenium is missing, Maven fetches it from the central repository. Testers save time because they do not download JAR files manually.
2. Maven Ensures Version Consistency
Different team members may use different machines. Maven eliminates version mismatch by enforcing the same Selenium dependencies for the entire team. This ensures stable automation testing results across environments.
3. Maven Updates Libraries Easily
You update Selenium by changing a version number in pom.xml. Maven handles the rest. You never track dozens of JAR files manually. This helps testers avoid outdated libraries and security risks. Testers in Selenium online training often practice version upgrades to learn how projects evolve over time.
4. Maven Supports Selenium Grid, TestNG, and JUnit
Most Selenium test frameworks use TestNG or JUnit. Maven manages those dependencies the same way. It also supports Selenium Grid libraries for distributed testing. This helps teams scale automation tests across machines.
5. Maven Helps Integrate Plugins for Reports and Execution
Common Maven plugins include:
-
Surefire Plugin: Runs TestNG or JUnit tests.
-
Failsafe Plugin: Supports integration tests.
-
Compiler Plugin: Sets Java version.
These plug-ins help testers run Selenium tests smoothly in local systems and CI/CD pipelines.
Understanding the pom.xml for Selenium Projects
A typical Maven pom.xml contains:
-
Project information
-
Dependencies
-
Build plugins
-
Test framework configurations
Below is a simple Selenium dependency block that most students practice early in a Selenium certification course:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>4.15.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Maven reads this file. Maven downloads the required Selenium WebDriver libraries. Maven places them into the project environment automatically.
If you use TestNG, you include:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>7.9.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
This step equips your project with Selenium and TestNG. It prepares you to build a test automation framework quickly.
Real-World Example: How Maven Supports Daily Automation Tasks
Let us explore a simple real-world scenario. A company wants to test its web application across Chrome and Edge. A tester runs the following steps:
-
Add Selenium and WebDriver Manager dependencies.
-
Add TestNG.
-
Add Surefire plugin for execution.
-
Run mvn test in terminal.
Maven downloads all required tools. Maven identifies conflicts. Maven ensures smooth execution. This process helps testers reduce setup time by almost 40%, according to industry surveys. Many professionals report improved collaboration because every team member uses the same pom.xml file.
Students learning through a Selenium course online or a selenium automation testing course apply the same steps. These skills prepare them for real project work in enterprises that demand automation software training.
Step-by-Step Guide: Create a Selenium Project With Maven
Follow these simple steps to create your first Selenium-Maven project:
Step 1: Install Java and Maven
Install JDK. Install Maven. Set PATH variables. These steps complete your environment.
Step 2: Create Maven Project
Use the command:
mvn archetype:generate
Select default archetype. Create project folder.
Step 3: Add Selenium Dependencies
Open pom.xml. Insert the Selenium WebDriver dependency block. Save the file.
Step 4: Add TestNG (Optional but Recommended)
Add TestNG dependency. TestNG offers annotation-based control. It supports parallel testing.
Step 5: Write Your First Selenium Script
Create a simple script:
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://example.com");
System.out.println(driver.getTitle());
driver.quit();
Place this inside the src/test/java directory.
Step 6: Run Tests With Maven
Use:
mvn clean test
Maven compiles code. Maven downloads libraries. Maven runs tests. This process helps testers practice stable execution cycles. These steps appear in many Online Selenium training sessions to introduce learners to industry workflows.
Why Organizations Prefer Maven for Selenium Automation
1. Predictable Builds
Maven gives predictable output. Testers get stable results. Teams reduce build failures.
2. Faster Onboarding
New team members clone a repository. They run Maven commands. No manual configuration is required. This saves significant training time.
3. Smooth CI/CD Integration
Companies use Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or Azure Pipelines. Maven integrates easily. It allows scheduled test runs. This supports continuous testing.
4. Easy Migration During Selenium Updates
Selenium releases updates regularly. Maven helps teams adopt changes quickly. A simple version change updates the framework.
Key Maven Features That Support Selenium Frameworks
Dependency Management
This is Maven’s strongest feature. It helps avoid version conflicts. It supports cleaner automation frameworks.
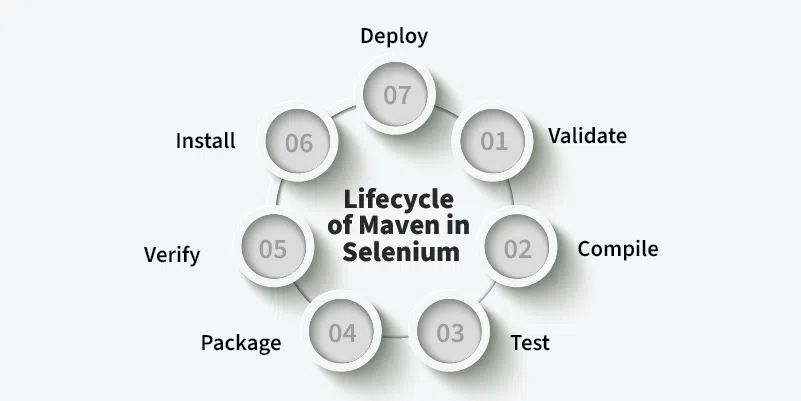
Build Life Cycle
Maven uses build phases such as validate, compile, test, package, and install. These phases give structure to automation tasks.
Plugin Integration
Plugins allow testers to extend the power of Maven. For example:
-
Run tests automatically
-
Generate reports
-
Trigger builds
-
Set Java versions
Central Repository Access
Maven uses a central repository. It ensures easy access to stable and updated Selenium libraries.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make When Using Maven With Selenium
Students in a Selenium testing course sometimes face issues because they make small configuration errors. Common mistakes include:
-
Incorrect dependency versions
-
Missing TestNG configuration
-
Wrong plugin versions
-
Incorrect directory structure
-
Missing WebDriver executables (when not using WebDriver Manager)
These mistakes cause runtime failures. Learners in Selenium online training practice troubleshooting steps to build confidence.
How Maven Supports Scalable Test Automation
Maven supports scaling in several ways:
Parallel Testing
With TestNG, Maven supports parallel execution. This reduces test cycle time significantly.
Cross-Browser Execution
Maven manages dependencies for Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Safari drivers.
Distributed Testing With Selenium Grid
Maven supports Selenium Grid libraries. Teams run tests across nodes. Selenium automation testing grows smoothly with this system.
Integration With BDD Tools
Maven supports Cucumber-JVM. This helps organizations adopt BDD-style automation.
Real Company Case Study (Simplified)
A digital banking company built a Selenium automation suite for its customer portal. The team used Maven for:
-
Dependency management
-
TestNG integration
-
Parallel execution
-
CI/CD pipeline triggers
The team improved automation stability by 65% after migrating from manual JAR management to Maven. New testers learned the system quickly because pom.xml provided clear structure. This simple change helped the company meet weekly release deadlines consistently.
Many students in Online Selenium training programs study similar real-world cases. It prepares them for industry expectations.
Hands-On Example: Full Maven pom.xml for Selenium
Below is a complete sample:
<project>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>automation.project</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-maven-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>4.15.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>7.9.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
This structure forms the backbone of most Selenium automation projects. Students in automation software training often work with such configurations daily.
Conclusion
Maven handles Selenium dependencies in a simple, reliable, and automated way. It manages versions, downloads libraries, supports plug-ins, and ensures stable test execution. You can start strong in automation when you understand Maven. You build better test frameworks. You grow faster in your Selenium career.
Start your learning today. Build your first Maven-Selenium project. Move one step closer to becoming a skilled automation tester.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spellen
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness



